What Are the Core Working Principles of a Level Transmitter Board?
What is the Function of a Level Transmitter Board
What Is a Level Transmitter Board and Why Is It Important?
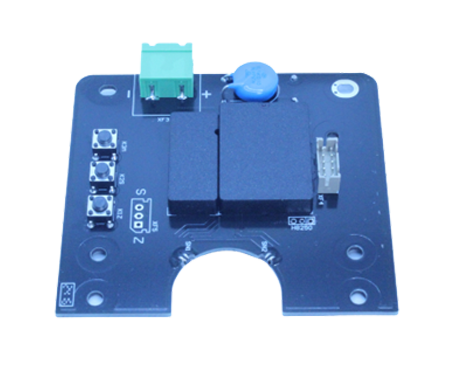
A level transmitter board is a key electronic module. It reads signals from level sensors to figure out the exact level of liquids or solid substances in industrial containers like tanks and silos. This component is crucial in process automation. Accurate and ongoing level monitoring is vital for safety, efficiency and operational control.
Level transmitters are devices that deliver continuous level measurement. They gauge levels of substances, such as water, thick fluids and fuels. To do this, the transmitter board turns raw sensor signals into standard outputs. Examples include 4–20 mA current loops or RS485 communication. These outputs integrate easily into industrial control systems like SCADA or PLCs.
How Does a Level Transmitter Board Operate Within a Measurement System?
The board works by getting input from different kinds of level sensors. These might be ultrasonic sensors, capacitive sensors, or hydrostatic pressure sensors, based on the application. Once it receives the raw data, the board handles it with various signal conditioning methods. These include amplification, filtering and analog-to-digital conversion.
The handled signal then comes out in analog or digital forms. This could be an analog 4-20mA, Modbus, or Ethernet. Such formats enable smooth integration into monitoring systems. This allows real-time data display and automatic control actions.

Key Components and Signal Processing Techniques
What Are the Core Electronic Components Found on a Level Transmitter Board?
A typical level transmitter board contains several basic components:
- Microcontroller or Signal Processor: It handles sensor data interpretation and runs algorithms for precise measurements.
- Analog-to-Digital Converter (ADC): It changes incoming analog signals into digital form for further processing.
- Voltage Regulators: They keep a steady power supply to support dependable operation.
- Communication Interfaces: Protocols such as Modbus, HART, or RS485 enable links with industrial systems.
These parts work closely together. They provide high precision and flexibility in various industrial environments.
How Does Signal Conditioning Improve Accuracy?
Signal conditioning boosts data trustworthiness. It does this by cutting out interference and adjusting for surrounding factors. Key elements include:
- Filters: They remove electrical noise that might warp sensor signals.
- Amplifiers: They boost faint input signals to make them readable.
- Temperature Compensation Circuits: They tweak readings on the fly to handle temperature-induced sensor shifts.
Thanks to unique algorithms and constant research efforts, our solutions help you stay current with industry changes. They support the technical growth of your products.
Types of Level Sensors Compatible with Transmitter Boards
Which Sensor Technologies Can Interface with a Level Transmitter Board?
Ultrasonic Sensors
Ultrasonic transducers sit at or near the top of a container. They send out an ultrasonic pulse. The pulse strikes the liquid’s surface and bounces back. The sensor then computes the fill level from the time between sending and receiving the signal. As a contact-free approach, ultrasonic sensors suit corrosive or dangerous materials. In these cases, direct contact with the sensor is not practical.
Capacitive Sensors
Capacitive level measurement relies on a shift in capacitance. An insulated electrode serves as one capacitor plate. The tank wall acts as the other plate. This setup works well for spotting both liquids and solids, like powders or grains.
Hydrostatic Pressure Sensors
A hydrostatic level sensor gauges the pressure in a liquid at a set depth. This method is popular in water treatment facilities and oil storage tanks. It proves reliable amid changing pressures.
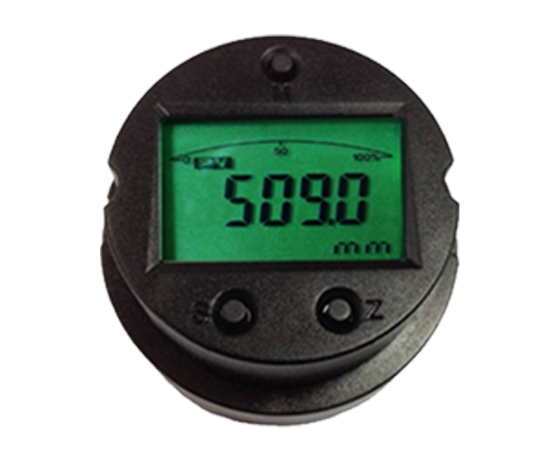

Output Formats and Integration with Control Systems
What Output Signals Are Commonly Used in Level Transmitter Boards?
Analog Outputs (4–20 mA)
This output resists electrical noise well over long distances. It suits transmitting precise measurements in tough industrial settings. The 4–20 mA signal is one of the most popular choices. Its simplicity and durability make it so.
Digital Outputs (Modbus, RS485)
Digital outputs like Modbus RTU over RS485 provide better features. These include far-reaching communication and sending several parameters at once. Our products fully match common protocols like HART and PROFIBUS-PA. They align with worldwide standards. This ensures easy integration and straightforward export.
How Do These Boards Communicate With Industrial Systems?
Level transmitter boards rely on standard protocols to connect with SCADA systems, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and cloud platforms. These connections guarantee smooth data exchange, real-time oversight and remote setup options.
Factors Affecting the Performance of Level Transmitter Boards
What Environmental Conditions Influence Signal Accuracy?
Surrounding elements can greatly affect measurement dependability:
- Temperature Fluctuations: They can alter sensor calibration and cause measurement drift.
- Electrical Interference: Without proper shielding, analog signals may capture electromagnetic noise.
Our automated production and testing systems, along with electronic barcode tracking, ensure steady performance for each board. This holds true even in big production runs.
How Does Material Type Impact Sensor Readings?
The physical traits of the material being measured also influence accuracy:
- Viscous or Foaming Materials: They can interfere with ultrasonic wave bounces.
- Conductive Materials: They need precise calibration with capacitive sensors to prevent wrong readings.
Applications Across Different Industries
Where Are Level Transmitter Boards Commonly Used?
Water and Wastewater Treatment Plants
They handle long-range measurements too. That’s why many ultrasonic transmitters appear in open tanks, sumps and reservoirs. The boards automate pump control based on tank levels. This helps avoid overflows or dry runs.
Food and Beverage Industry
Exact level measurement maintains steady ingredient mixing in batch production processes.
Oil & Gas Sector
Level transmitter boards track fuel and lubricant storage in harsh environmental conditions. From oil & gas to pharmaceuticals, power generation and offshore platforms, our boards see wide use in tough industrial settings. They help clients make big strides in the market.
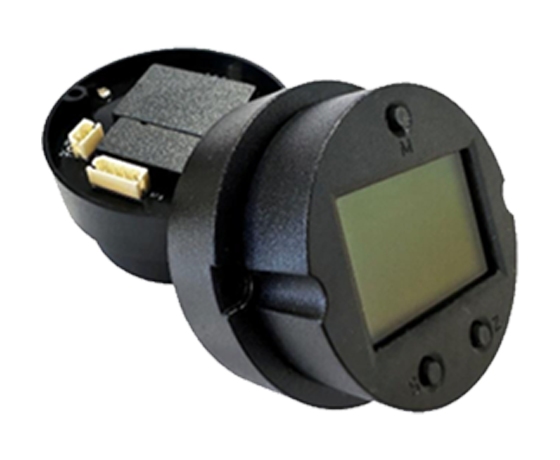
Introduction to ICwalk’s Level Transmitter Board Solutions
Who Is ICwalk and What Makes Their Level Transmitter Boards Reliable?
At ICwalk, we focus on making high-quality electronic parts for industrial automation. ICwalk transmitter boards earn trust from more than 800 instrument makers in China. They have strong real-world testing.
Our level transmitter boards feature solid signal processing abilities. This ensures dependable measurements in difficult working conditions.
We back various sensor types, including capacitive, ultrasonic and hydrostatic. We also provide several output choices, like 4–20 mA analog signals and RS485 digital communication. These meet diverse integration requirements.
What Features Distinguish ICwalk’s Level Transmitter Boards?
Advanced Signal Conditioning
Built-in filters, amplifiers and temperature compensation circuits improve measurement steadiness. These elements offer toughness against environmental shifts and electronic disturbances.
Compatibility & Integration
We support a broad array of sensors for pressure, temperature, level and flow. Our boards also feature HART communication support. This allows easy linking to global-standard industrial systems.

FAQ
Q: What is the difference between a level transmitter board and a level sensor?
A: A level sensor detects the actual physical level of a substance, while the transmitter board processes this raw data into usable signals for monitoring systems.
Q: Can one level transmitter board work with different types of sensors?
A: Yes, many modern boards are designed to be compatible with multiple sensor technologies as long as they meet input specifications.
Q: Why is 4–20 mA output preferred in industrial applications?
A: It offers strong resistance to electrical noise over long distances, making it ideal for transmitting accurate measurements in industrial environments.
Related Posts
-
How to Ensure Longevity of Pressure Control Boards in Transmitters?
December 26,2025
-
How Do You Select the Right Flow Transmitter Board for Your Application Needs?
January 01,2026
-
How to Assemble a Flowmeter Faster and More Accurately
October 16,2025