How Is Signal Processing Achieved in Flow Transmitter Circuit Boards?
The Basics of Signal Processing in Flow Transmitter Circuit Boards
What Is a Flow Transmitter Circuit Board and Why Is Signal Processing Important?
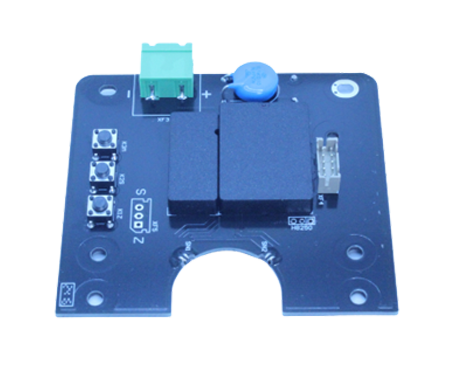
A flow transmitter circuit board is a dedicated electronic setup. It handles the task of turning raw signals from flow sensors into standard, practical output signals. These outputs usually show the flow rate of fluids—either liquid or gas—inside a pipeline or channel. This setup allows exact control and oversight in industrial settings.
Signal processing plays a vital role in these boards. It makes sure the sensor signal is precise, steady, and dependable. It does this by cutting out noise, boosting faint signals, and changing them into common formats. Proper signal processing prevents erratic measurements from things like outside disturbances, sensor differences, or electrical static. Thus, signal processing forms the base for reliable flow information.
Key Components Involved in Signal Processing
The main parts of a flow transmitter circuit board consist of microcontrollers or digital signal processors (DSPs). These handle control logic and perform calculations. Analog-to-digital converters (ADCs) turn analog inputs from sensors into digital form. Operational amplifiers adjust the signal with gain changes or buffering.
Filters—such as low-pass and high-pass types—are added to block unwanted noise frequencies. These filters prove crucial in tough industrial spots where electromagnetic interference (EMI) happens often. Combining these parts lets the board handle signals correctly and reliably, even in difficult situations.

How Does a Flow Transmitter Circuit Board Process Signals?
What Happens When a Sensor Detects Flow?
When a flow sensor spots fluid movement in a pipe or channel, it creates an analog voltage or current signal. This signal matches the speed or amount of fluid moving through. Then, this basic analog signal goes to the flow transmitter circuit board. There, it gets analyzed and improved.
How Are Analog Signals Conditioned and Converted?
The initial step involves boosting the signal with operational amplifiers. This boosting raises the detail level and confirms that small flow changes get noticed properly. After that, filtering occurs to clear out electrical noise and even out any sudden jumps or uneven spots in the data.
With the signal now prepared, it moves to an ADC. This device shifts it into a digital version. The digital data can then be handled by built-in software or microcontrollers. They use smart methods to fine-tune and figure out the flow rate exactly.
How Is the Final Output Signal Generated?
Once processing finishes, the microcontroller shapes the details into standard industry output signals. Examples include 4–20 mA current loops or digital methods like Modbus RTU or HART. These outputs matter for sending live data to programmable logic controllers (PLCs), SCADA systems, or display panels. From there, further steps or views can happen.
ICwalk’s E4000 ซีรีส์ provide adaptable output choices. These include 4 – 20mA current output and digital communication protocols such as HART and MODBUS. This setup aids smooth links to control and monitoring systems.
Factors That Affect Signal Accuracy in Flow Transmitter Boards
What Are Common Sources of Signal Distortion?
A few things can twist signals in a flow transmitter circuit board. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) from close machines or power supplies can add extra frequencies that mess up the main signal. Changes in temperature also impact electronic parts. This might lead to shifts in readings. Plus, bad grounding or shielding can cause ground loops or sudden voltage jumps that harm data quality.
How Can These Issues Be Minimized?
Designers use various fixes to cut down these problems. Shielded cables and smart PCB arrangements help lower EMI risks. Software routines for temperature adjustment can be added to the firmware. They tweak readings on the fly as heat shifts occur.
Isolation setups guard against ground loops and voltage surges. This keeps signal clearness intact and shields the circuit board and linked systems from harm.

Integration of Digital Technologies in Flow Transmitter Boards
How Do Modern Flow Transmitters Use Digital Processing?
Current flow transmitter boards, like those from ICwalk, make use of advanced digital signal processing methods. These handle instant filtering, checks, and mistake fixes. Such features improve signal quality and support stronger data analysis, even amid noise.
Our unique signal processing and adjustment models beat local rivals. They deliver ±0.1% accuracy in tough spots. This lets our transmitters perform outstandingly in many industrial cases.
Also, our software-driven systems allow wireless updates. This means better performance and new features without changing the hardware.
What Are the Advantages of Digitally Processed Signals?
Signals handled digitally bring many perks. They achieve top accuracy thanks to clever filtering routines. Setup becomes simpler with visual software tools. Plus, check features grow stronger, like self-tests and warnings for upkeep ahead of time.
Our automatic making and testing processes, along with electronic barcode following, ensure solid work for each board. This holds true even in big production runs.
ICwalk’s Flow Transmitter Circuit Board Solutions
สิ่งที่ทำให้ ICwalk’s Flow Transmitter Boards Stand Out?
At ICwalk, we bring more than 16 years of know-how in providing top-notch flow transmitter circuit boards. We help customers in 50+ countries with OEM parts and clever modules that match worldwide rules like HART and PROFIBUS-PA. Our answers rely on special patented algorithms for unmatched exactness, even where interference runs high.
ICwalk transmitter boards earn trust from over 800 instrument makers in China. They have broad real-world proof. We back several output types, including 4–20 mA, RS485/Modbus RTU, pulse frequency outputs, and HART too. This fits easily into your setups.
Our flexible designs simplify customizing for different sensor kinds. These cover electromagnetic, vortex, ultrasonic, or metal tube float-based tools.
Which Applications Can Benefit from ICwalk’s Products?
ระบบอัตโนมัติอุตสาหกรรม
Our boards give steady results for automated lines. They keep calibration spot-on over time with little shift. ICwalk boards secure precise flow checks in automated process lines. They show minimal drift as time passes.
สิ่งอำนวยความสะดวกในการบำบัดน้ำ
In water plants, fluid pressure can change a lot. Our strong signal tuning keeps readings firm across all work conditions. Dependable signal tuning aids in watching flow rates under shifting pressure levels.
HVAC Systems
Due to their small build and keen response, our transmitter boards suit HVAC setups well. There, airflow needs close watching. Compact design and high sensitivity make ICwalk boards perfect for adding into air handling systems.

คำถามที่พบบ่อย
Q: What type of signals do flow transmitter circuit boards typically output?
A: Most flow transmitter boards output standard analog signals like 4–20 mA or voltage levels (0–10V), as well as digital protocols such as Modbus or pulse/frequency outputs depending on application needs.
Q: Why is filtering important in a flow transmitter circuit board?
A: Filtering removes unwanted electrical noise that could distort measurement accuracy, especially in industrial environments with high EMI.
Q: Can I use one flow transmitter board design across different types of sensors?
A: Yes, modular designs like those offered by ICwalk allow compatibility with various sensor types by adjusting gain settings, input ranges, or firmware configurations accordingly.